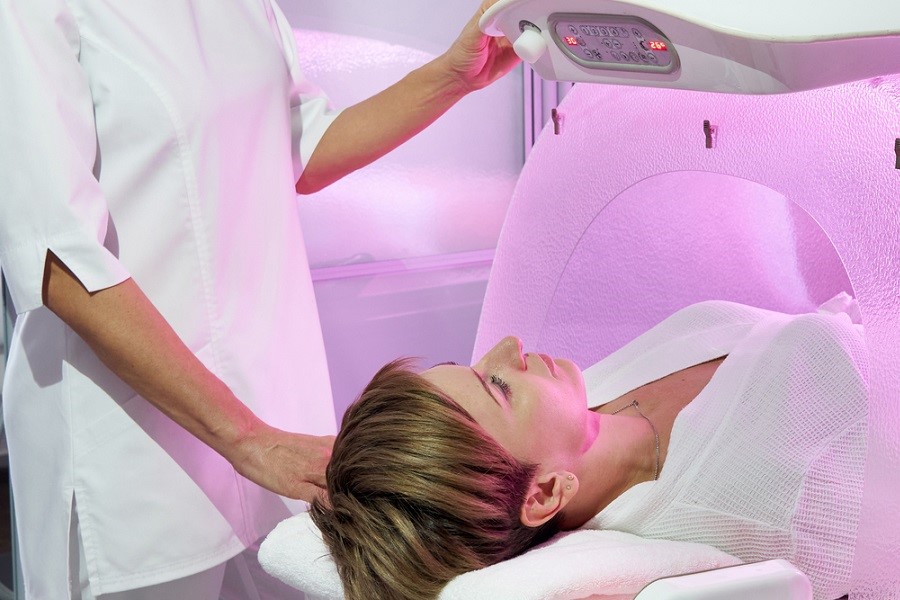
Halotherapy – relaxation and recovery in a salt cave.
One of the key features of the air in a salt cave is the saturation of oxygen with ions and the absence of bacteria and viruses. Salt vapors have a beneficial effect on the respiratory and immune systems.
Visitors to halo chambers after several procedures note a decrease in the level of fatigue, an improvement in well-being and mood.
Climatotherapy sessions in a salt cave give the following results:
- Hemoglobin increases
- Blood circulation improves
- Immune processes are activated
- Emotional state stabilizes
- Bronchi and lungs are cleared of bacteria and viruses
- Hormonal levels return to normal
- Skin regeneration starts
- Metabolism improves
Gas therapeutic baths – steam carbon dioxide and dry carbon dioxide.
When carrying out the carbon dioxide bath procedure the human body is exposed to a mixture of water vapor with concentrated carbon dioxide. Steam expands the pores on the skin, which promotes better absorption of CO2 and its penetration into the body. Within a few hours after taking a bath, active gas exchange processes occur, as a result of which the blood and tissues are enriched with oxygen.
Carbon dioxide bath is considered one of the effective methods for stimulating blood circulation; it is recommended for rehabilitation for people who have suffered a myocardial infarction and have chronic diseases of the cardiovascular system. The bath is also prescribed for people with endocrine disorders, reduced immunity, and respiratory diseases. A steam carbon dioxide bath perfectly fights the signs of aging; after a course of procedures, the quality of the skin significantly improves.
The dry carbon dioxide bath procedure goes like this: you sit in a special bath where dry carbon dioxide is supplied. This gas easily penetrates human skin and dissolves in the blood plasma, improving oxygen exchange in tissues and expanding the walls of blood vessels. Also, dry carbon dioxide baths have a positive effect on the functions of the central nervous system.
When exposed to carbon dioxide, blood vessels dilate and peripheral resistance decreases, and blood pressure decreases accordingly. A course of dry carbon dioxide baths can lead to stable remission in hypertension.
Carbon dioxide has an antioxidant effect, so such baths are an excellent prevention of aging. This gas has a primary stimulating effect on the nervous system, and subsequently — calming. This combination helps cope with chronic fatigue syndrome.
When taking dry carbon dioxide baths the interaction of insulin with muscle tissue improves, thereby reducing blood sugar levels. Therefore, a course of such baths is indicated for diabetes and obesity.
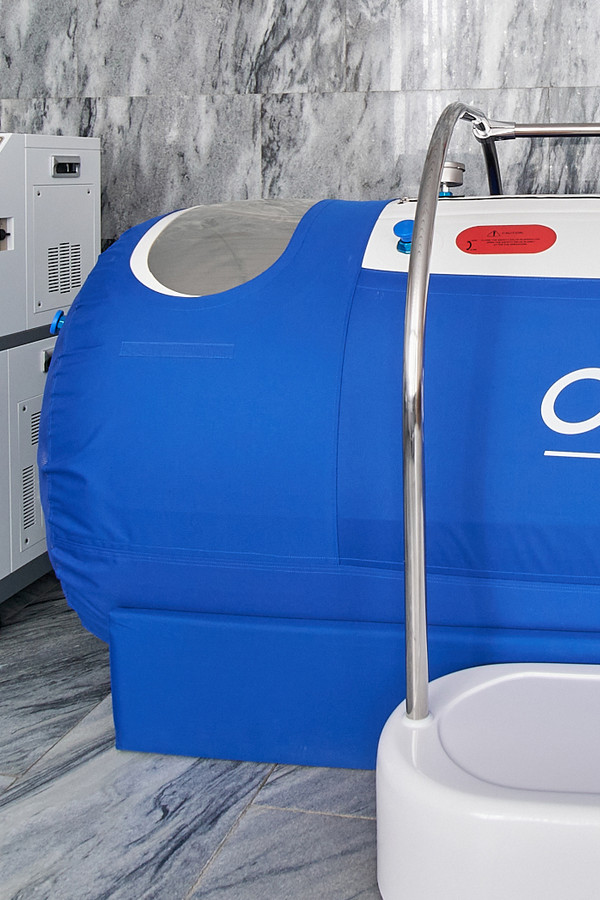
Hypoxytherapy (mountain air) - a treatment method using inhalation of air similar in composition to mountain air.
During a course of hypoxic therapy, the body's resistance to various pathogenic factors of the external and internal environment significantly increases due to its preliminary training to oxygen deficiency (hypoxia). In the practice of treating a number of diseases, training for hypobaric high-altitude and pressure-chamber hypoxia has long been used.
A course of normobaric hypoxic therapy has a positive effect on the processes of oxygen metabolism and the acid-base state of the body.
Hypoxytherapy has a normalizing effect on the carbohydrate, fat, protein and electrolyte spectra of the blood, increases the anti-inflammatory potential, activates the activity of the vital systems of the body and has a positive effect on its vitality.
Inhalations – one of the main methods of treatment and prevention of respiratory diseases and acute respiratory viral infections. It is also used for diseases of the heart and blood vessels, gastrointestinal tract, and nervous system. The effectiveness of the procedure is achieved by direct impact on the mucous membranes of the respiratory system with drugs converted into an aerosol.
Inhalations – introduction of drugs into the body through the respiratory system using a special nebulizer – nebulizer. Fine powders, gaseous substances and liquid aerosols, when inhaled through the nose or mouth, penetrate deeply into the lungs, evenly settle on the mucous membranes, and are then distributed through the bloodstream to organs and tissues.
Other facilities
- Medicine Service
- Food
- Spa & Sport
- Comfortable stay
- For kids
- Documentation



.svg)
.svg)